Gout Care
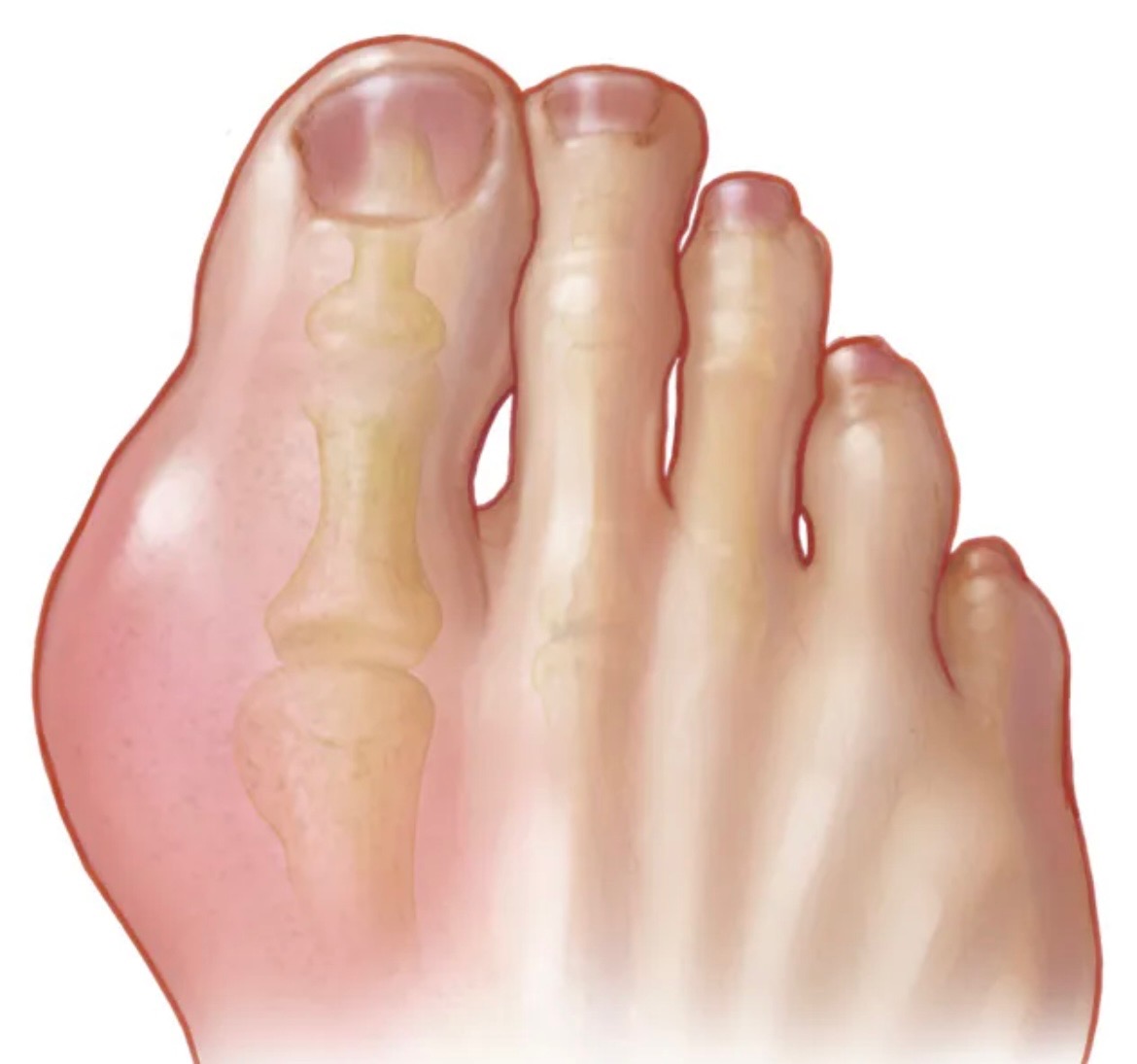
Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by sudden, severe attacks of pain, swelling, and redness in the joints, commonly affecting the big toe. It is caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the blood, which can form sharp, needle-like urate crystals in a joint or surrounding tissue, leading to intense pain and inflammatory symptoms.
Causes of Gout
Gout results from a combination of dietary, genetic, and environmental factors that lead to hyperuricemia, or high levels of uric acid in the blood:
- Diet: Consumption of foods rich in purines (such as red meat, seafood, and alcohol, especially beer) can raise blood uric acid levels.
Genetics: A family history of gout increases the risk.
Medical conditions: High blood pressure, chronic kidney disease, diabetes, and obesity can predispose individuals to hyperuricemia.
Medications: Certain medications, such as diuretics (used to treat hypertension) and low-dose aspirin, can increase uric acid levels.
Age and Sex: Gout is more common in men than women and typically affects middle-aged individuals.
Symptoms of Gout
Gout symptoms can develop suddenly and are often severe, including:
- Pain: Gout usually affects one joint at a time, often the big toe, ankle, or knee. The pain is usually severe within the first four to twelve hours.
Swelling and Redness: The affected joint becomes swollen, tender, warm, and red.
Limited Range of Motion: As gout progresses, people may not be able to move their joints normally.
Treatments for Gout
Treatment for gout aims to reduce pain during attacks and prevent future episodes, involving medications and lifestyle changes:
Medications:
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Drugs like ibuprofen and naproxen reduce inflammation and pain.
Colchicine: An anti-inflammatory specifically used for gout, effective at reducing gout pain when taken within 24 hours of an attack.
Corticosteroids: Prednisone may be used for patients who cannot take NSAIDs or colchicine.
Uric Acid-Lowering Therapy: Medications such as allopurinol and febuxostat are used to lower blood uric acid levels and prevent gout attacks.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies:
Dietary Changes: Avoiding foods high in purines and consuming plenty of water can help reduce uric acid levels.
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of gout.
Limiting Alcohol and Sugary Drinks: Especially beers and drinks sweetened with high-fructose corn syrup.
Exercise: Helps improve overall health and weight control.
Get the best gout treatment here at the office of Dr. Lana Schikman. Please give us a phone call or request an appointment today in the form below.

